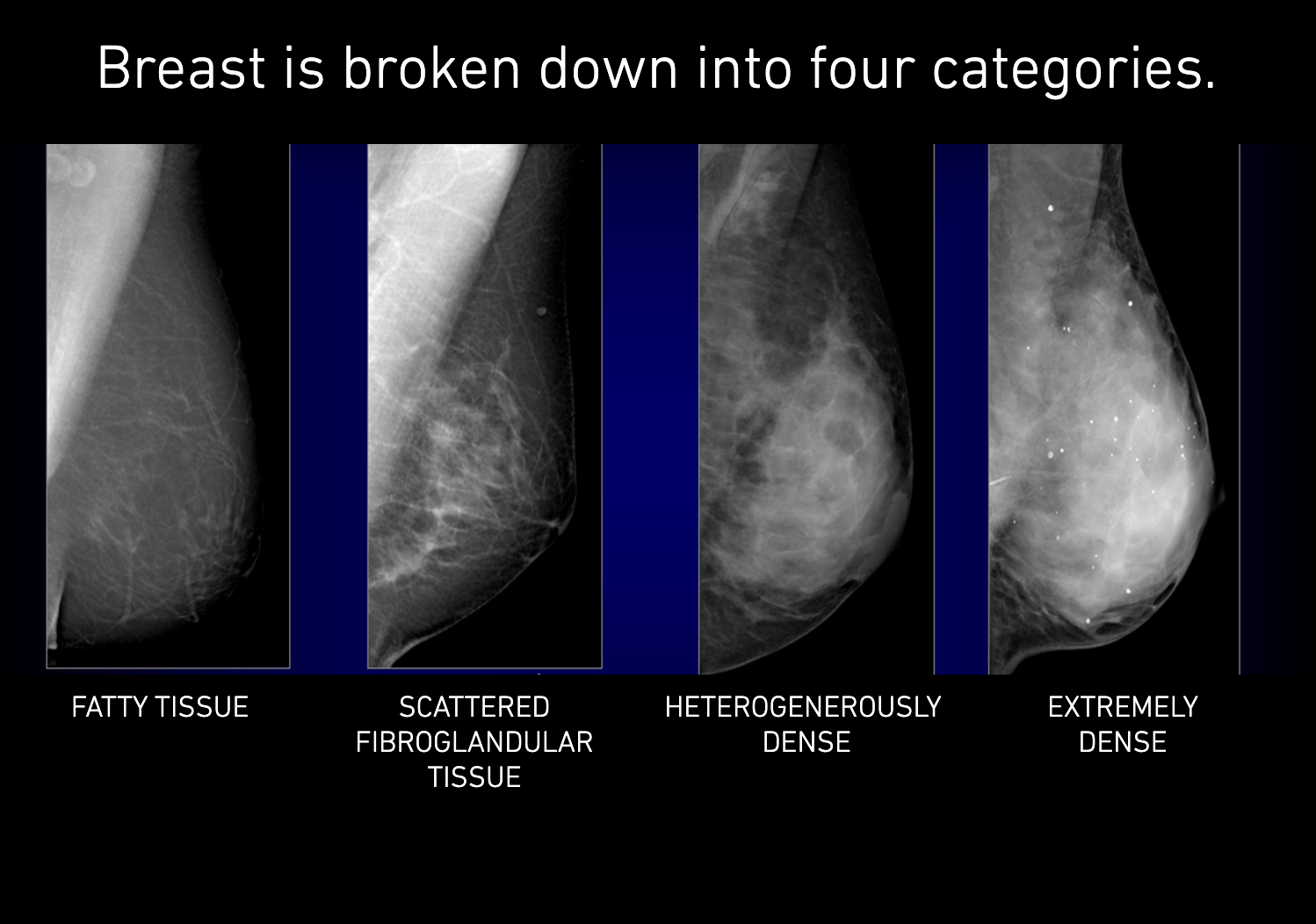
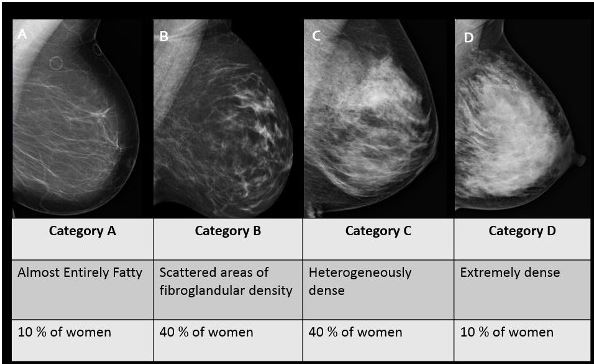
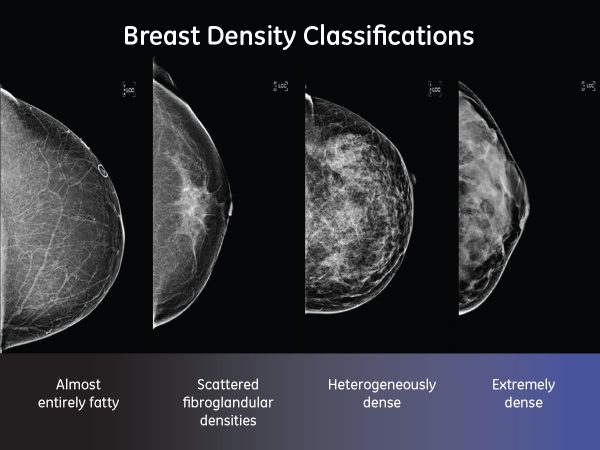
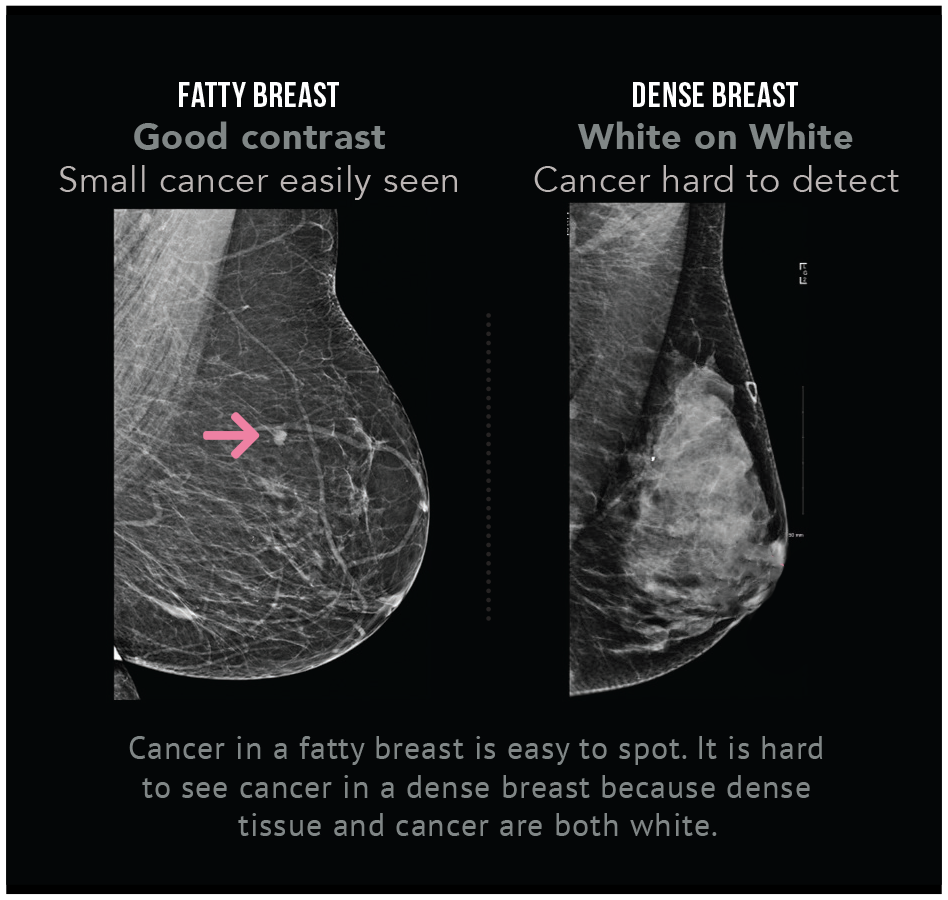
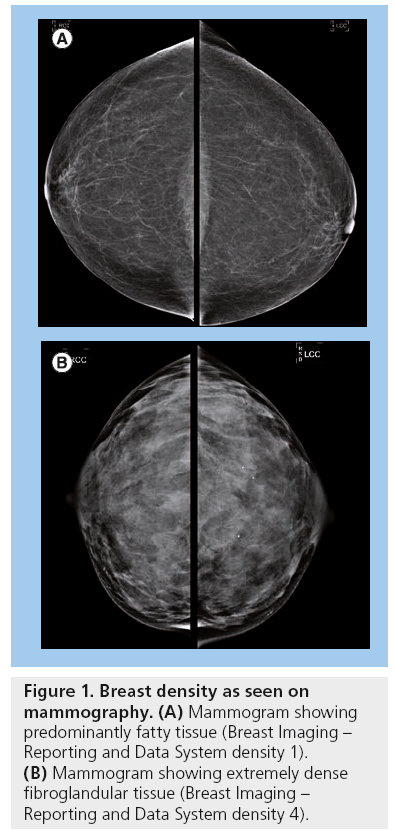
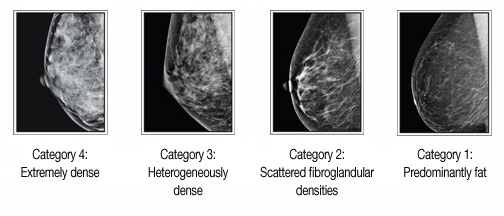
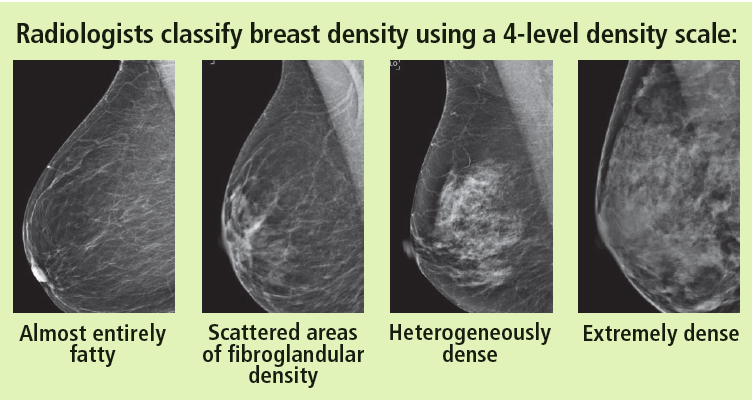
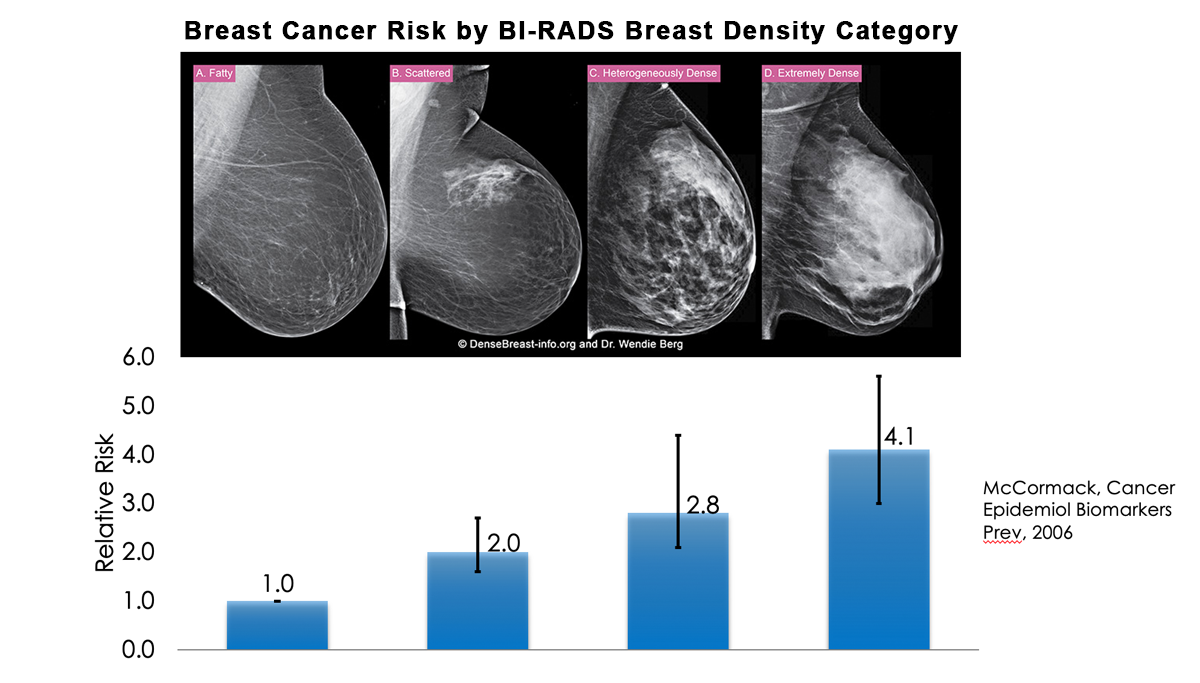
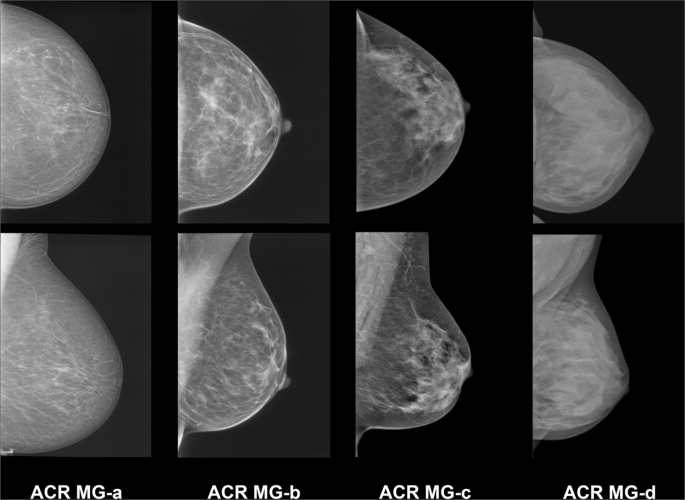
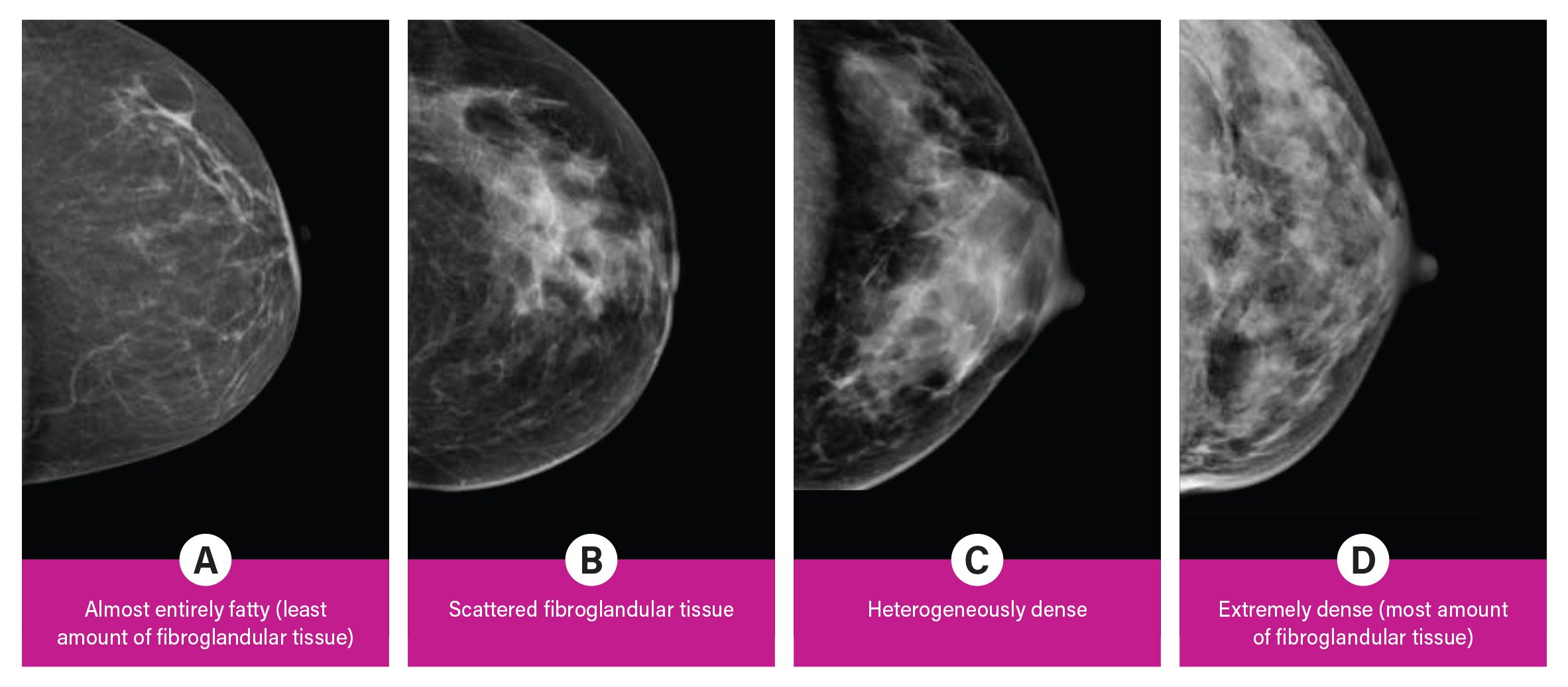
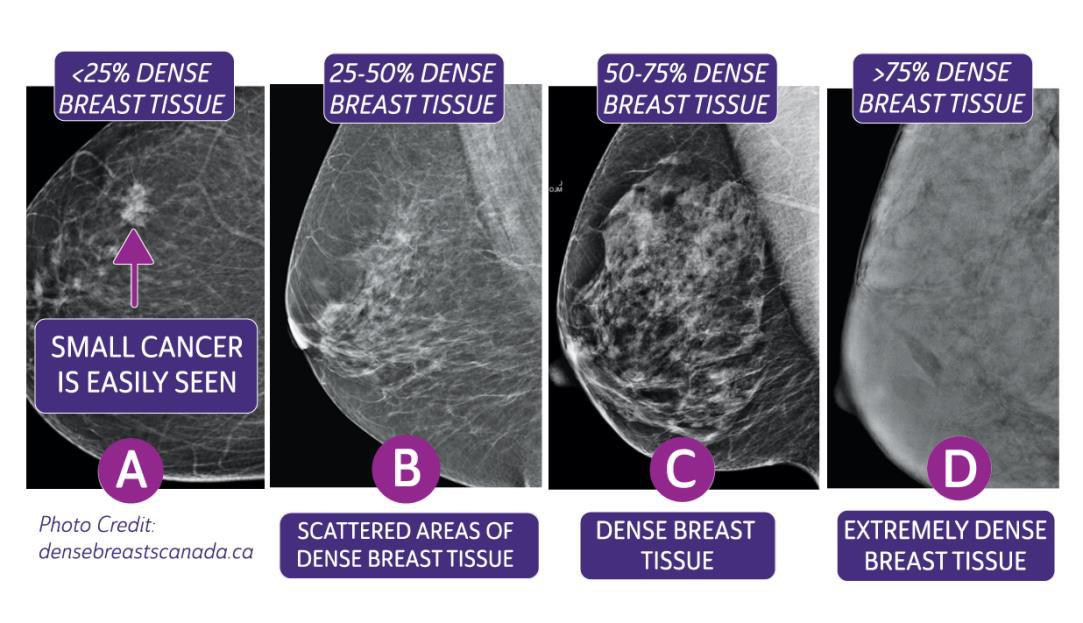
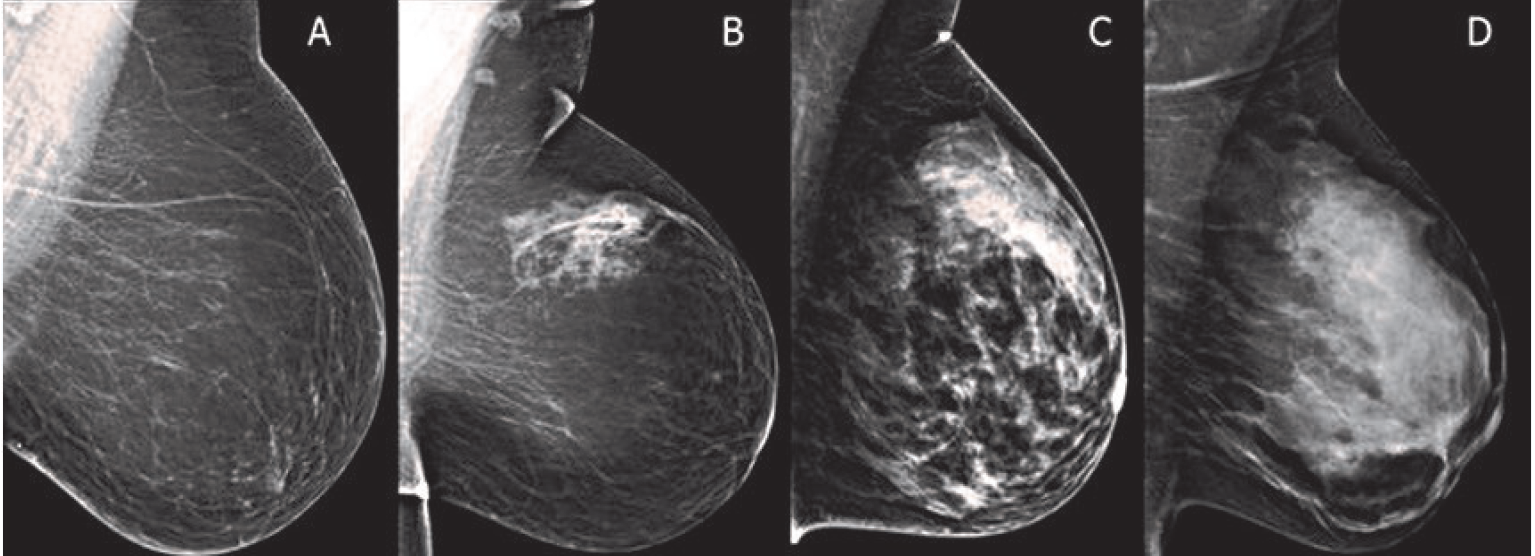
In clinical practice in the United States, Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BIRADS) breast density categories are used in mammographic reports to indicate the degree of mammographic breast density a) The breasts are almost entirely fatty, b) There are scattered areas of fibroglandular density, c) The breasts are heterogeneously dense, which may obscure small masses, and d) The breasts are extremely dense Heterogeneously dense – A breast has more fibrous and glandular tissue This can make it more difficult for a radiologist to detect cancerous changes in a mammogram Extremely dense – A breast has a high amount of fibrous and glandular tissue Because breast masses can sometimes blend in with dense, healthy tissue in a mammogram, cancer canBreast density Levels 1 and 2 are considered "nondense" due to the high proportion of fatty tissue The high proportion of fat in Levels 1 and 2 density breasts makes breast cancer detection easier because fat appears gray on a mammogram whereas cancer appears white Therefore, it's easy to detect a white cancer against a gray background

Breast Density Carolina Breast Imaging Specialists
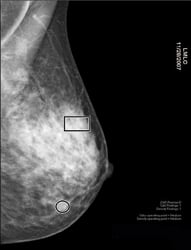
Heterogeneously dense stage 1 breast cancer mammogram
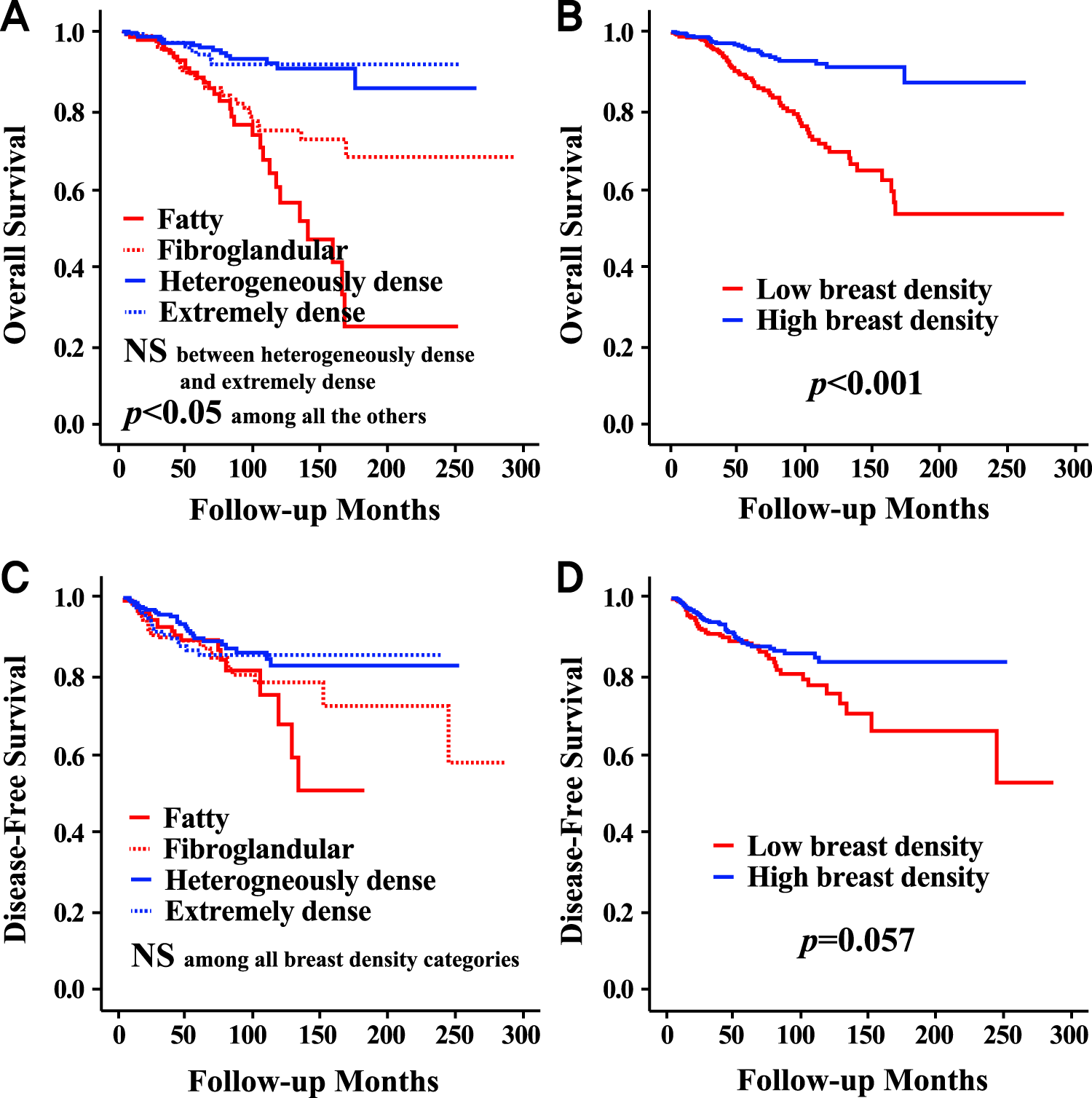
Heterogeneously dense stage 1 breast cancer mammogram- Women with dense breast tissue had twice the odds of having an interval cancer diagnosis compared with women with nondense breasts Those women did not tend to have a worse prognosis, but womenAccording to the National Cancer Institute, nearly 50% of all women age 40 and older have dense breasts Like Joan, many women don't know whether they have dense breasts or what that means Knowing whether you have dense breasts is important because women with dense breasts have a higher risk of developing breast cancer, and often need




Breast Density What Is It And What Does It Mean For Me Breast360 Org The American Society Of Breast Surgeons Foundation
– At least heterogeneously dense breast tissue – Elevated risk for breast cancer • Personal or family history of breast cancer • Prior breast biopsy demonstrating atypia • BRCA 1/2 gene mutations • Prior chest radiation between ages 10 and 30 – Evaluated screening whole breast ultrasound in conjunction with mammography "By the time the cancer would have been picked up by a mammogram, it could have been stage two or three By recommending a second screening, Dr Ann Steiner saved my life," Reisboard said Reisboard is among the more than 400 asymptomatic women with dense breasts who underwent abbreviated magnetic resonance imaging (also called "fast MRStage breast cancer within weeks of a 'normal' mammogram It was at this time that I learned that I had dense breast tissue and wasn't aware of its significance as 1) Mammography misses every other cancer in dense breasts as cancer appears white on a mammogram and dense tissue is whitethus there is no contrast to see the cancer and 2) the
Women with dense breasts are at increased risk of breast cancer, and high breast density is a cause of falsenegative results on a standard screening mammography However, results from a new study suggest that breast density alone should not dictate whether women should receive additional screening for breast cancer after a normal result on a screening mammogram5 Facts to Know Breast density is determined through a woman's mammogram and described as one of four categories depending on the amount of breast tissue in comparison to fat in the breast; M = Metastases M0 means that cancer has not metastasized (spread to other areas of the body) Verywell / Gary Ferster Thus, using the TNM system, stage 1 cancers are defined as follows Stage 1 Breast Cancers Stage 1A T1N0M0 The tumor is less than mm (2 cm) in size and there is no spread to lymph nodes
I have dense breast tissue – and women like me (2/3 of premenopausal and 1/4 of post menopausal) have less than a 48% chance of having breast cancer detected by a mammogram In November 03 I had my yearly mammogram and my "Happy Gram" report that I received stated that my mammogram was "NORMAL" and that there were "no significant findings" Dense breast tissue makes it difficult to spot cancers on mammograms, and increases your cancer risk have heterogeneously dense breasts, you're 162 times more likely than average to develop40% of women age 40 and over have dense breasts Cancer is 4 times more likely in women with extremely dense breasts than in women with fatty breasts



Automated Whole Breast Ultrasound Barbara Hayden Dense Breasts




Four Iowa Women Share Their Stories Of Breast Cancer Survival
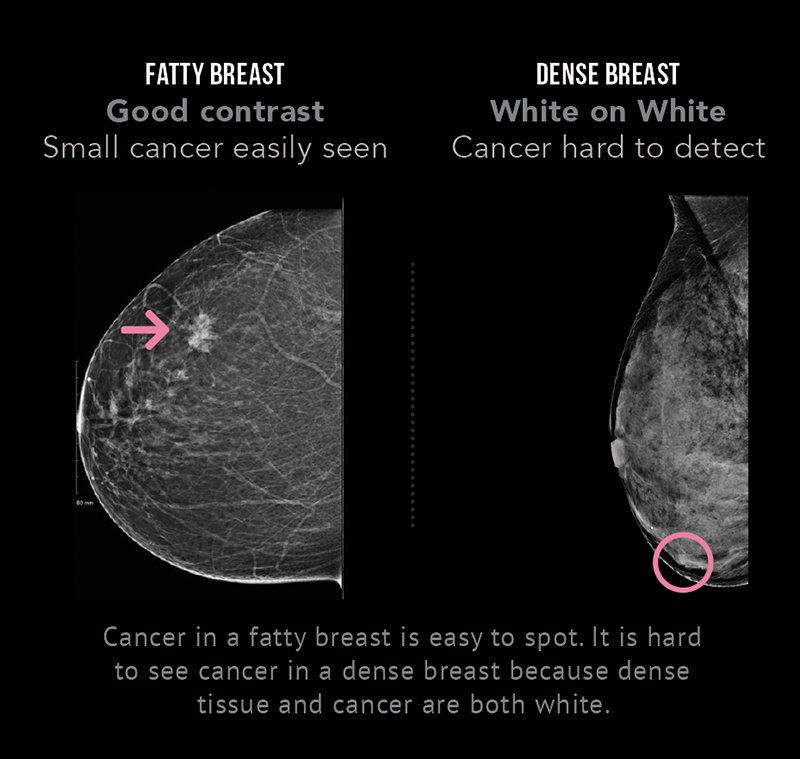
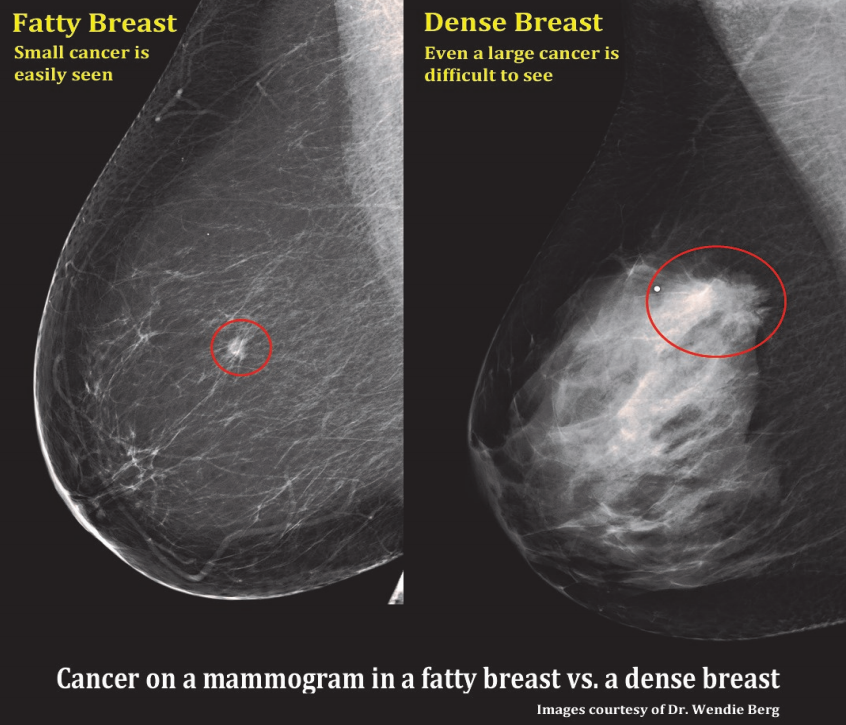
Dense breasts also make it more difficult for radiologists to see a small breast cancer because these growths can be overshadowed by the dense or white appearing tissue on a mammogram So dense breasts pose a "doublewhammy" of increased risk and decreased ability to#2 Increased Breast Cancer risk • Women with heterogeneously dense breasts & extremely dense breast tissue may have higher risk of breast cancer compared to women with lower density breasts • Extremely Dense vs Fatty – 46x • Risk of breast cancer in dense vs scattered density is about 1This means that you have moderately dense tissue, which is common and not a cause for concern Sometimes, dense tissue can make it difficult to accurately read a mammogram




Mammography 3d Mammography Tomosynthesis Densebreast Info Inc




Do You Have Dense Breasts Carolina Parent
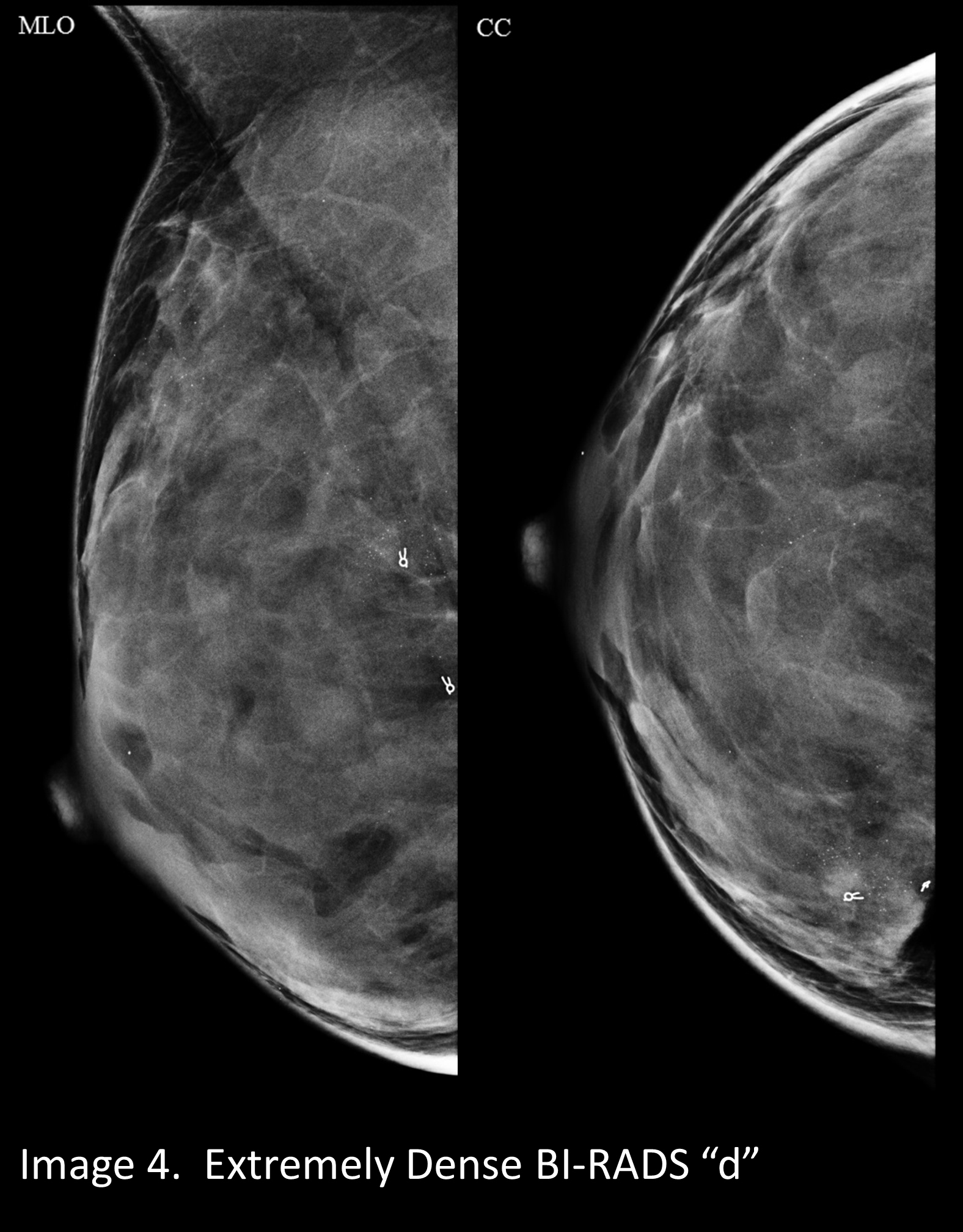
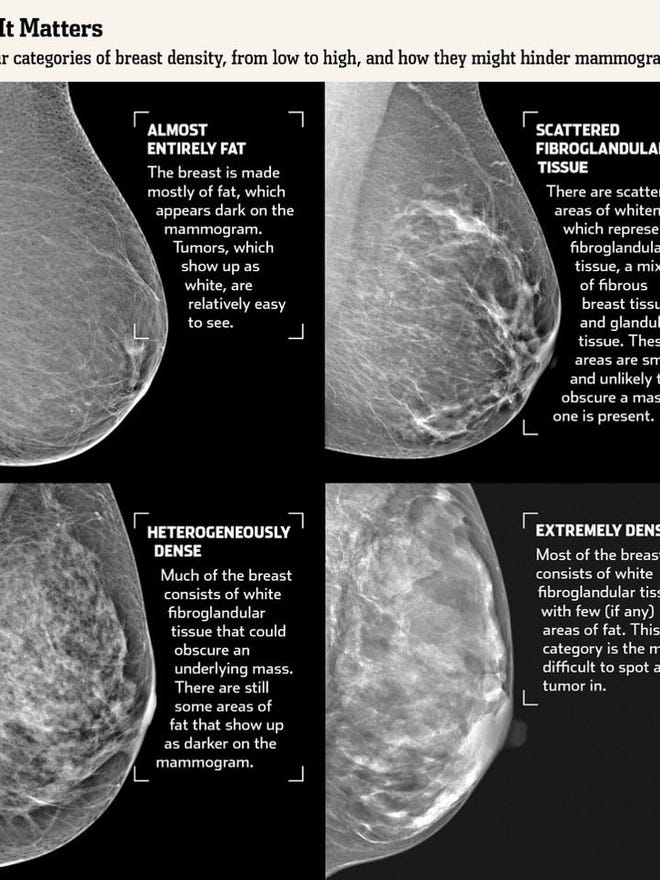
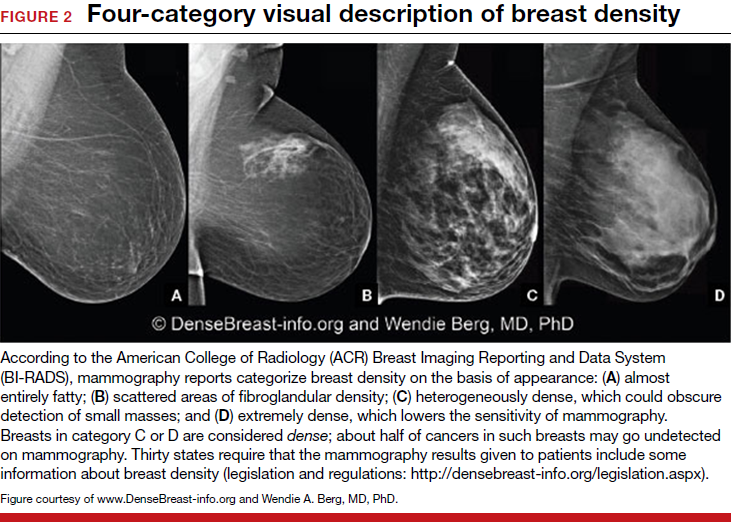
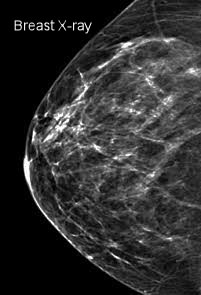
The breast tissue is heterogeneously dense, which could obscure detection of small masses (approximately 51% 75% glandular) 4 It is also a wellestablished predictor of breast cancer risk The common convention is that women who have greater than 50 percent density are considered to have dense breast tissue, namely heterogeneously and extremely dense About 40 percent of women of mammographic screening age are 'dense' Woman must understand that if she has denseBreast density refers to the amount of glandular and fibrous tissue Dense breasts have mostly glandular tissue, with just a little fat tissue A woman's breast density can change through her life There are four types of breast density, from most to least dense Extremely dense Heterogeneously dense



Mammogram Images Understanding Your Results



Automatic Breast Ultrasound State Of The Art And Future Perspectives Ecancer
My mammogram described my breasts as being "heterogeneously dense, which may obscure small masses" What does that mean? If a recent mammogram showed you have dense breast tissue, you may wonder what this means for your breast cancer risk Doctors know dense breast tissue makes breast cancer screening more difficult and it increases the risk of breast cancer Review your breast cancer risk factors with your doctor and consider your options for additional breast cancer "By the time the cancer would have been picked up by a mammogram, it could have been stage two or three patients with heterogeneously or extremely dense breast tissue, with a negative




Breast Density Carolina Breast Imaging Specialists




Breast Density And Mammogram Reports Dense Breast Tissue
"1st mammogram rt breast indeterminate mass all else clear breasts heterogeneously dense imaging incomplete 2nd mammo 12/5 what does this mean scared!" Answered by Dr Kenny Chuu Mammogram Hi Sorry to hear you are feeling so anxious When we see "i So fibrous tissue and ductal tissue looks white on a mammogram, and so does cancer When a woman is young, under 50, or premenopausal, the breasts are more dense according to the mammogram When you get older, the breasts become mostly fat and are easy to see through When a breast is easy to see through, it's easier to detect cancers Based on your unique information, Breastcancerorg can recommend articles that are highly relevant to your situation Calcifications are small deposits of calcium that show up on mammograms as bright white specks or dots on the soft tissue background of the breasts The calcium readily absorbs the Xrays from mammograms




Why Breast Density Matters Prevent Breast Cancer



Get Smart About Dense Breasts Mdedge Obgyn
Extremely dense "About 50 percent of women have heterogeneously dense or extremely dense breast tissue, which makes it more difficult to find breast cancer on a standard 2D mammogram," she said According to Dr Morris, dense breast tissue and cancer both are white on a mammogram, so breast density notifications were intended by law to Rest assured, breast density is not an independent risk factor for breast cancer, but rather a biomarker of risk, says Grady "Breast density can make detecting cancer on a mammogram much harder However, dense breast tissue can make it harder to find cancer on a mammogram and may also be associated with an increased risk of breast cancer heterogeneously dense breast tissue (5175% glandular) extremely dense (>75% glandular) Breast density is subjective



1



Your Patient Got A Dense Breast Notification With Her Mammogram Report What Are You Supposed To Do Christianacare News
The interval breast cancer population had a significantly more radiodense parenchymal pattern than the screeningdetected group (p < ) A significant trend was seen for younger women to have a more dense mammographic parenchymal pattern in both the screeningdetected and interval breast cancer groups (p = 0004 and < , respectively) Facts about Breast Density Having "heterogeneously dense breasts" does not put you at at significantly increased risk for breast cancer Having" extremely dense" breast tissue may have a minimal increased risk for breast cancer As breast density increases, the sensitivity often associated with a mammogram is often reduced The A large study of 40,000 women with extremely dense breasts in the Netherlands, called DENSE (Dense Tissue and Early Breast Neoplasm Screening), found that breast MRI was able to pick up some early breast cancers that had been missed after a mammogram returned normal results However, breast MRI also had an 8% falsepositive rate — meaning that it indicated a




Breast Density And Mammogram Reports Dense Breast Tissue



The Relationship Between Breast Density Age And Mammographic Lesion Type Among Chinese Breast Cancer Patients From A Large Clinical Dataset Bmc Medical Imaging Full Text
Probably OK Standards for mammography results recently changed, with expert guidelines now advising that patients be informed if dense tissue makes it harder to see small abnormalties However, the risk of this usually is very low If you are at special risk (eg strong family history of breast cancer), your insurance may cover MRI to assure all is wellIn Stage 1 breast cancer, cancer is evident, but it is contained to only the area where the first abnormal cells began to develop The breast cancer has been detected in the early stages and can be very effectively treated Stage 1 can be divided into Stage 1A and Stage 1BBreast cancer risk Research also shows that breast density can itself be a risk factor for developing breast cancer For the approximately 40 percent of women who have 'heterogeneously dense breasts' (Type C on the BIRADS scale), the risk of developing breast cancer is thought to be 12 times greater than average



Cureus Diagnostic Accuracy Of Digital Mammography In The Detection Of Breast Cancer
%20.png)



What Is Breast Density And Why Does It Matter Our Voices Blog Cbcn
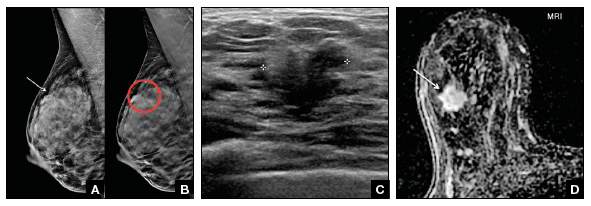
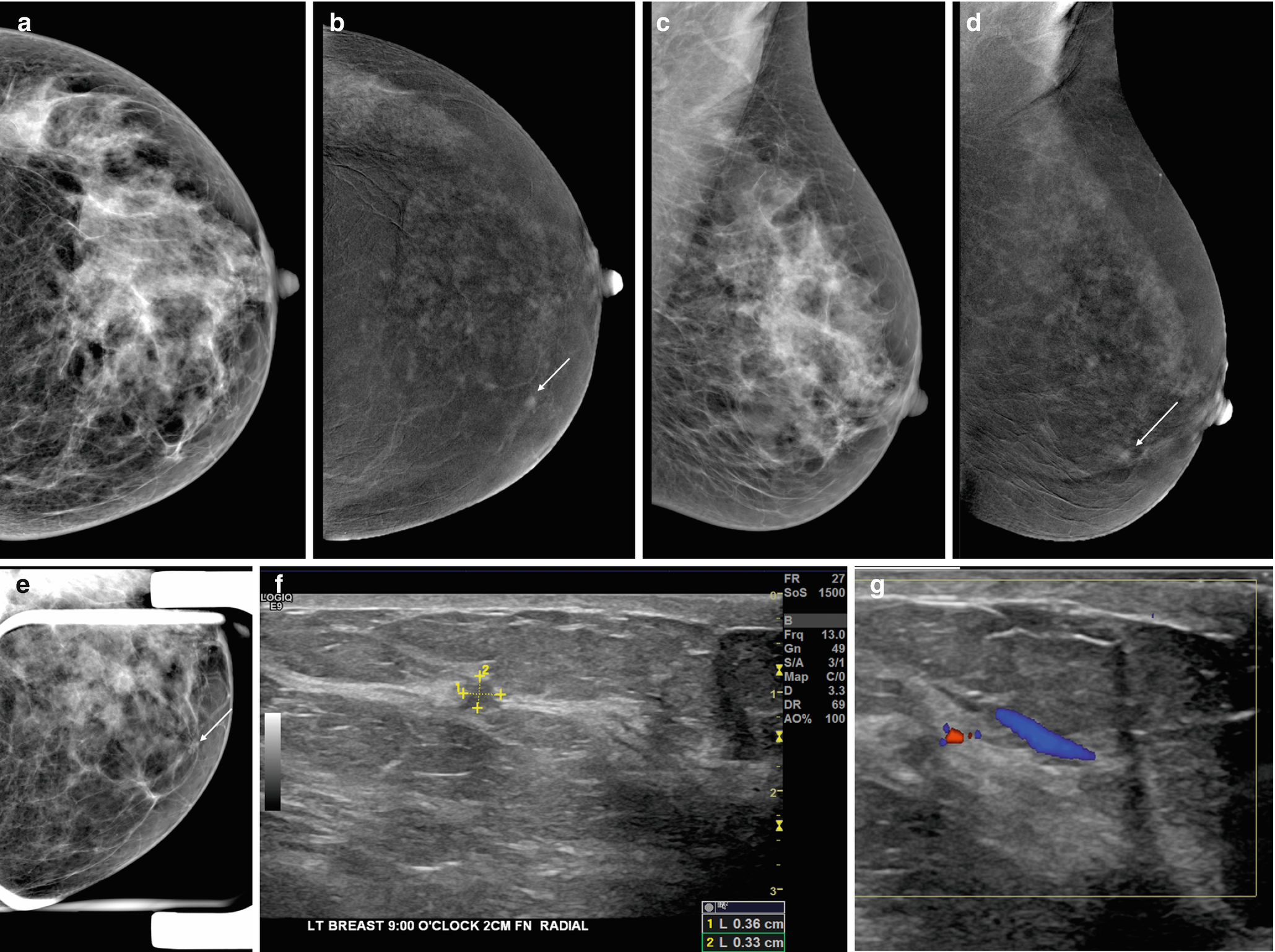
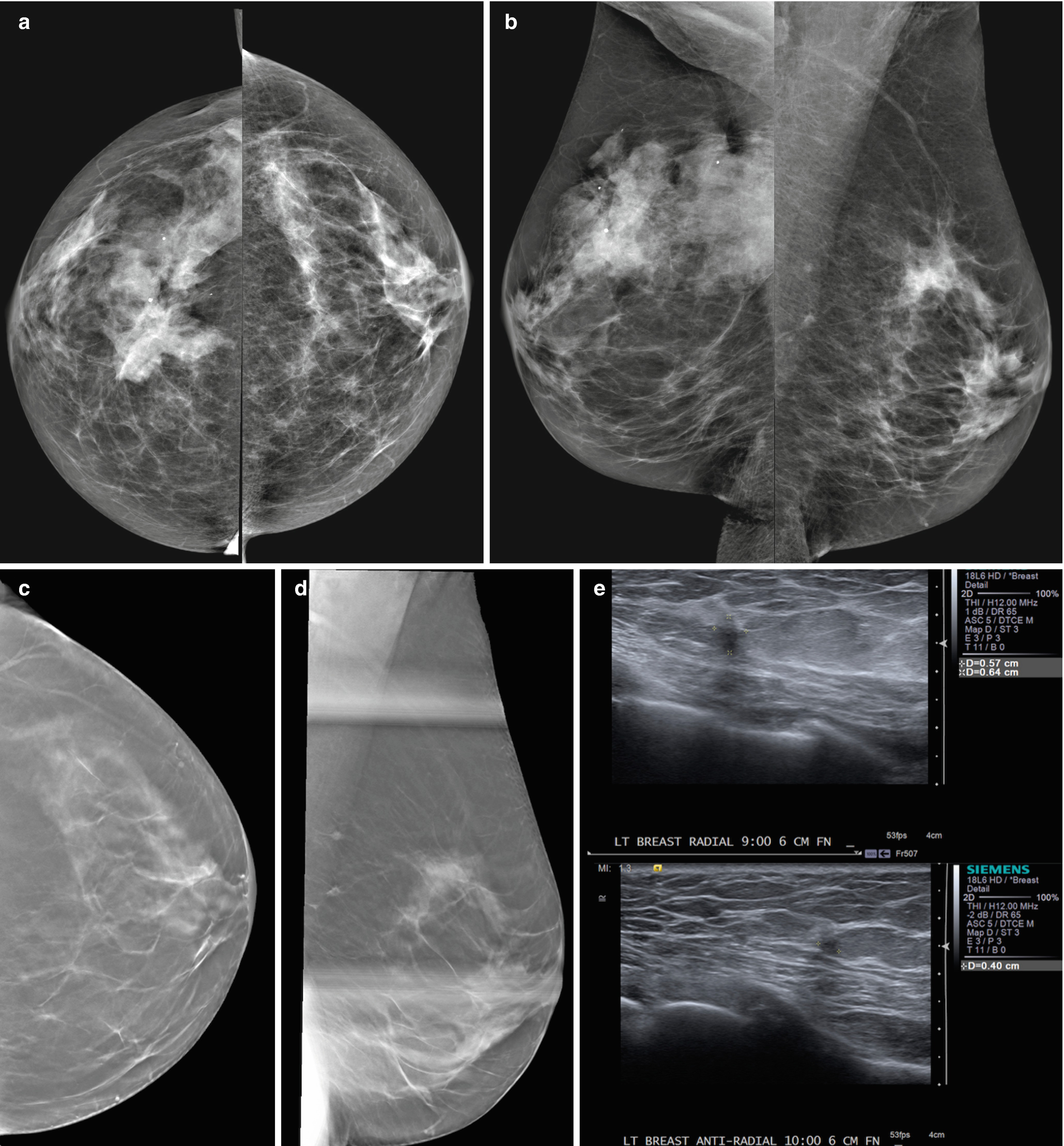
Risk for interval cancer were women with extremely dense breasts and Gail model 5year breast cancer risk of >167% or women with heterogeneously dense breasts and 5year risk of >250% (9) Even when breast cancer is detected at screening, women with dense Stage T1c, N0, M0 stage 1 left breast cancer IMAGING FINDINGS A 2dimensional (2D) mammogram revealed heterogeneously dense breast tissue without focal masses or asymmetries and without changes when compared to earlier mammograms (Figure 1) A 3dimensional (3D) mammogram revealed an area of architectural distortion in the lateral aspect Mom of Two Shares Shocking Breast Cancer Diagnosis Just Months After Normal Mammogram 'I Call Myself a Future Survivor' both breasts is heterogeneously dense This may lower the sensitivity



Blog How Dense Are You New Research Shows That Not All Dense Breasts Pose An Increased Cancer Risk



Vt Will Require Alerts About Breast Density
Low advanced cancer rates ( Women who have dense breast tissue, either heterogeneously dense or extremely dense, in addition to other risk factors for breast cancer may need additional breast cancer screening tests A simple If cysts are present on mammogram, they are definitely not cancer If the radiologist think the mass may be solid, because of the shape and the ultrasound results, then it might need a biopsy The breast mammogram in the image, certainly appears to have a nodule of some sort, but since it may or may not be a real nodule, one could label it as an 'asymmetric




Dense Breast Tissue And Breast Cancer Risk



Breast Health Archives Patricia Bowden Luccardi
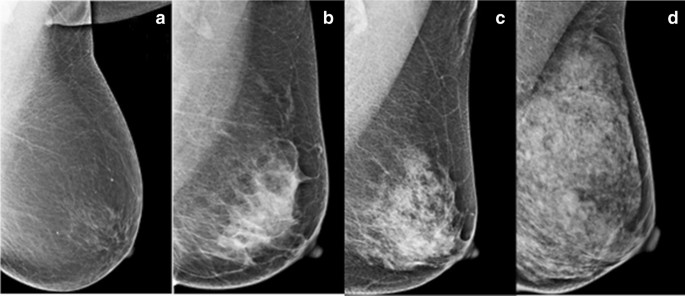
Breast tissue is composed of milk glands, milk ducts and supportive tissue (dense breast tissue) and fatty tissue (nondense breast tissue) Radiologists use mammogram images to grade breast tissue based on the proportion of dense to nondense tissue According to the BIRADS reporting system, the levels are (from left to right) almost entirely fatty, scattered areas of fibroglandular density,8 rows Your mammogram report will also include an assessment of your breast density, which is a description of how much fibrous and glandular tissue is in your breasts, as compared to fatty tissue The denser your breasts, the harder it can be to see abnormal areas on mammograms (Having dense breasts also raises your risk of getting breast cancer) The breast densitybreast cancer connection Women whose breasts appear dense on mammograms have a higher risk for some aggressive breast cancers One of the strongest known risk factors for breast cancer is high breast density — that is, relatively little fat in the breast and more connective and glandular tissue, as seen on




Breast Density What Is It And What Does It Mean For Me Breast360 Org The American Society Of Breast Surgeons Foundation



Breast Density Why Is It Important Lake Medical Imaging The Villages Florida
On a mammography report, breast density is assigned to one of the following four categories— The breasts are almost entirely fatty (about 10% of women) A few areas of dense tissue are scattered through the breasts (about 40% of women) The breasts are evenly dense throughout (about 40% of For women aged 50 to 64 years with heterogeneously or extremely dense breasts, the RR is 129, and for women aged 65 to 74 years, it is 130 7 However, women with dense breasts who develop breast cancer do not have an increased risk for dying from the disease, after adjustment for stage, treatment, method of detection, and other risk factorsImaging Findings A 2dimensional (2D) mammogram revealed heterogeneously dense breast tissue without focal masses or asymmetries and without changes



Diagnosis And Staging Of Breast Cancer When And How To Use Mammography Tomosynthesis Ultrasound Contrast Enhanced Mammography And Magnetic Resonance Imaging Springerlink



The Medical Minute Breast Density Separating Myth From Fact Penn State Health News
More of the breast is made of dense glandular and fibrous tissue (described as heterogeneously dense ) This can make it hard to see small tumors in or around the dense tissue Breasts are extremely dense, which makes it hard to see tumors in the tissue Mammogram reports sent to women often mention breast density Heterogeneously dense breasts is a term used in mammography to describe breasts with a higher percentage of glandular and supportive tissue than fat It occurs in 40% of women and while normal, can make it more difficult to detect breast cancer on mammography Dr



Get Informed Dense Breasts Canada Find Out Your Breast Density
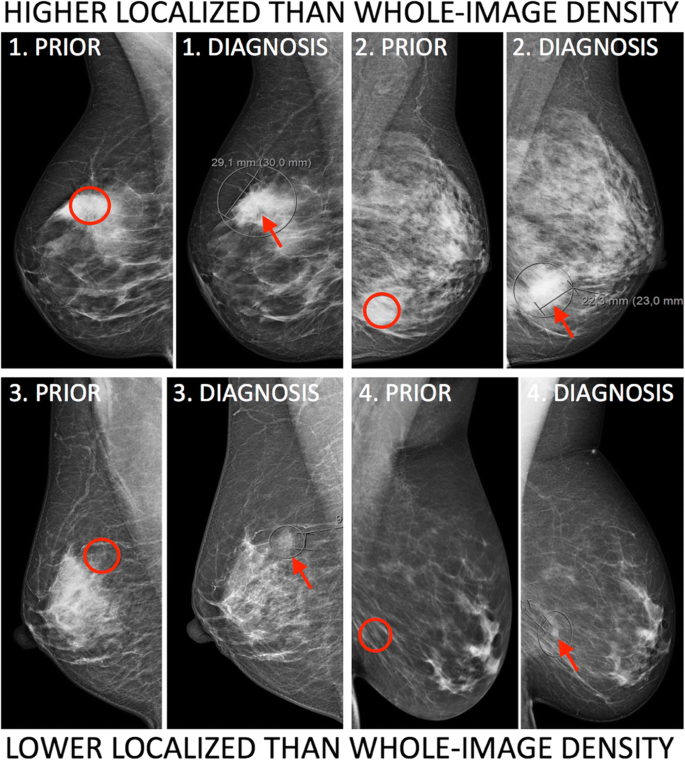



Localized Mammographic Density Is Associated With Interval Cancer And Large Breast Cancer A Nested Case Control Study Breast Cancer Research Full Text




Study Shows Breast Density Is Most Common Risk Factor For Breast Cancer



Dense Breasts Breast Cancer Risk And Screening Choices In 19 Healthmanagement Org




How 3d Mammograms Help Find Hidden Cancers Cleveland Clinic




Dense Breasts Advocacy Science And Cancer Dr Elisabeth Poorman



Diagnosis And Staging Of Breast Cancer When And How To Use Mammography Tomosynthesis Ultrasound Contrast Enhanced Mammography And Magnetic Resonance Imaging Springerlink




Breast Cancer Topic I Am Sure I Have Cancer And My Doctors Won T Listen



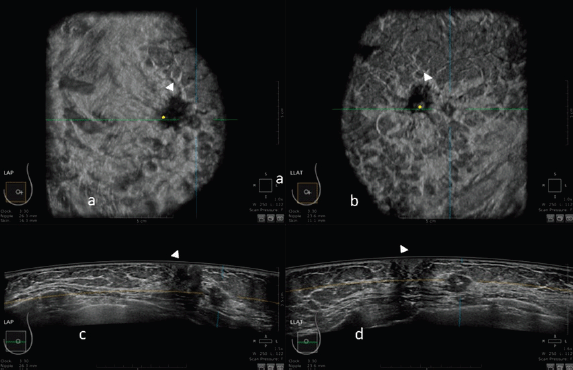
Automated Breast Ultrasound A Novel Approach To Screening Women With Dense Breasts
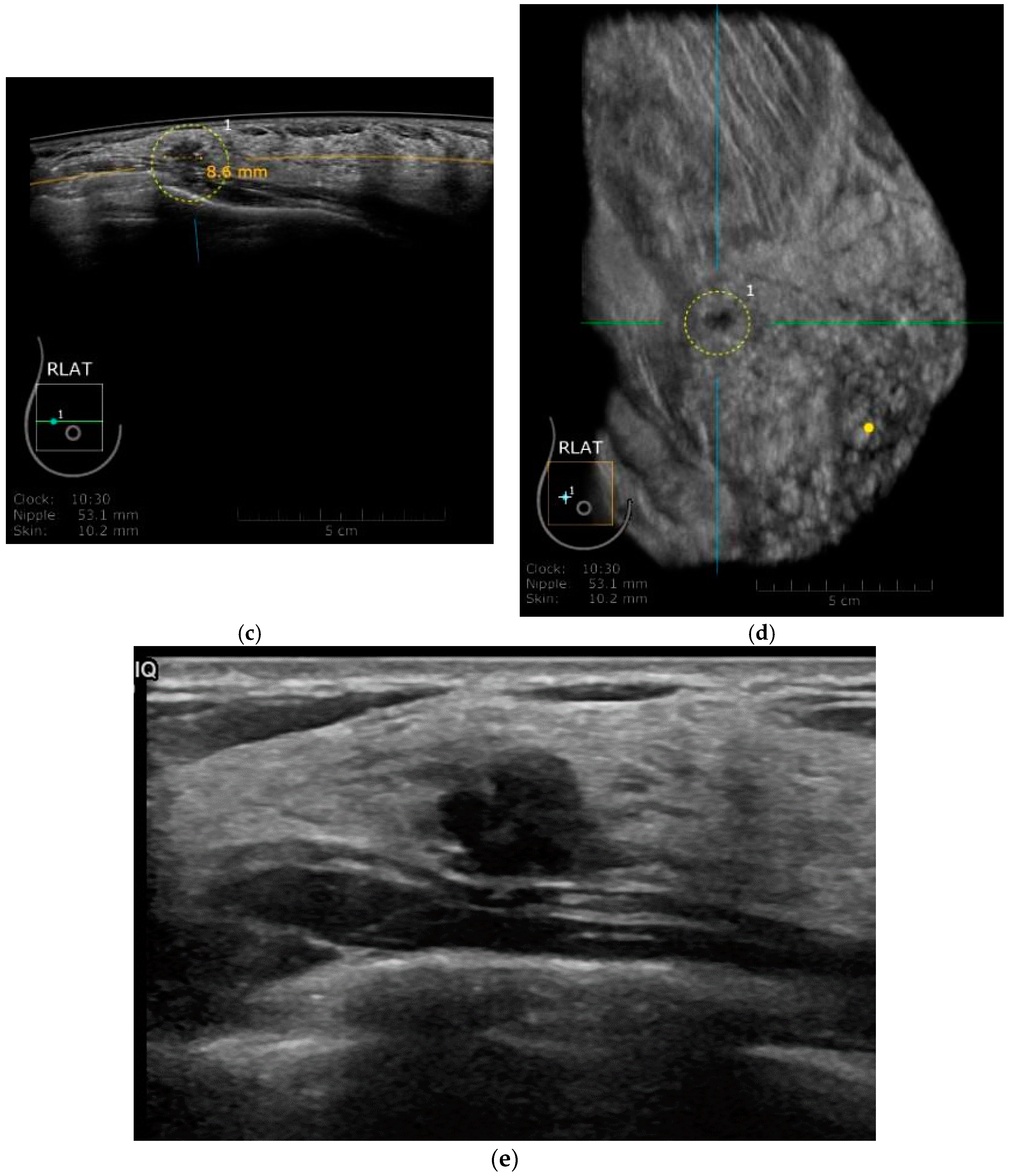



Diagnostics Free Full Text The Role Of Ultrasound In Screening Dense Breasts A Review Of The Literature And Practical Solutions For Implementation Html




Be The Change You Wish To See In The World Being Dense



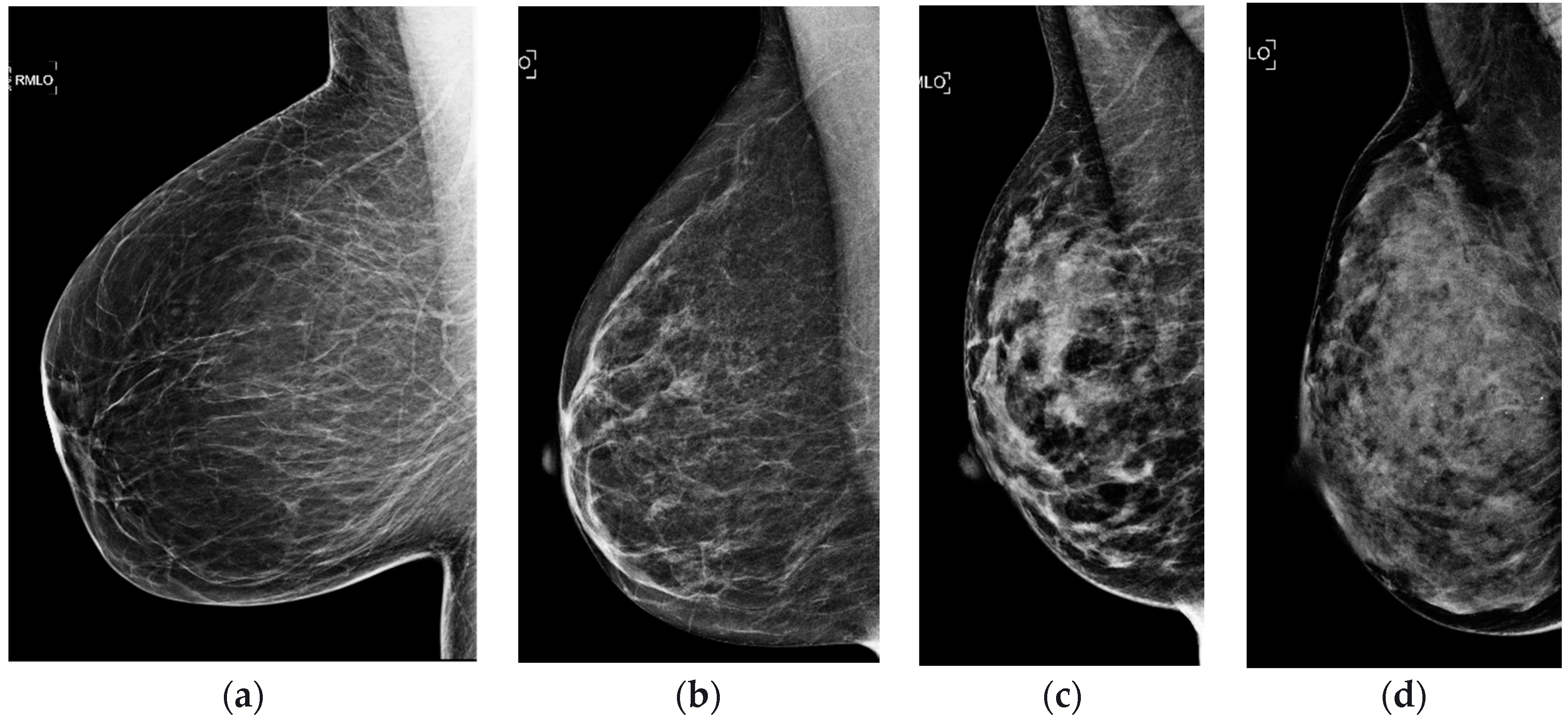
Some Example Mammograms Showing Various Birads Density Classification Download Scientific Diagram



3d Abus Santa Fe Imaging




Mammographic Density And Screening Breast Health And Awareness Breast Cancer Network Australia




A Review Of Breast Density Implications And Breast Cancer Screening Clinical Breast Cancer



Diagnostics Free Full Text The Role Of Ultrasound In Screening Dense Breasts A Review Of The Literature And Practical Solutions For Implementation Html



What Is Breast Density How Does It Affect Cancer Screening



Prognostic Influence Of Preoperative Mammographic Breast Density In Operable Invasive Female Breast Cancer Scientific Reports



Breast Density And Optimal Screening For Breast Cancer Mdedge Obgyn



Breast Density Canadian Cancer Survivor Network



Dense Breast Tissue What You Need To Know Mayo Clinic Health System



Health Care Provider Faqs Densebreast Info Inc



Www Edusymp Com Esi Cbic16 1 Cbic16 Syllabus Pdf



Http Www Mayoclinicproceedings Org Article S0025 6196 14 5 Pdf



Your Patient Got A Dense Breast Notification With Her Mammogram Report What Are You Supposed To Do Christianacare News




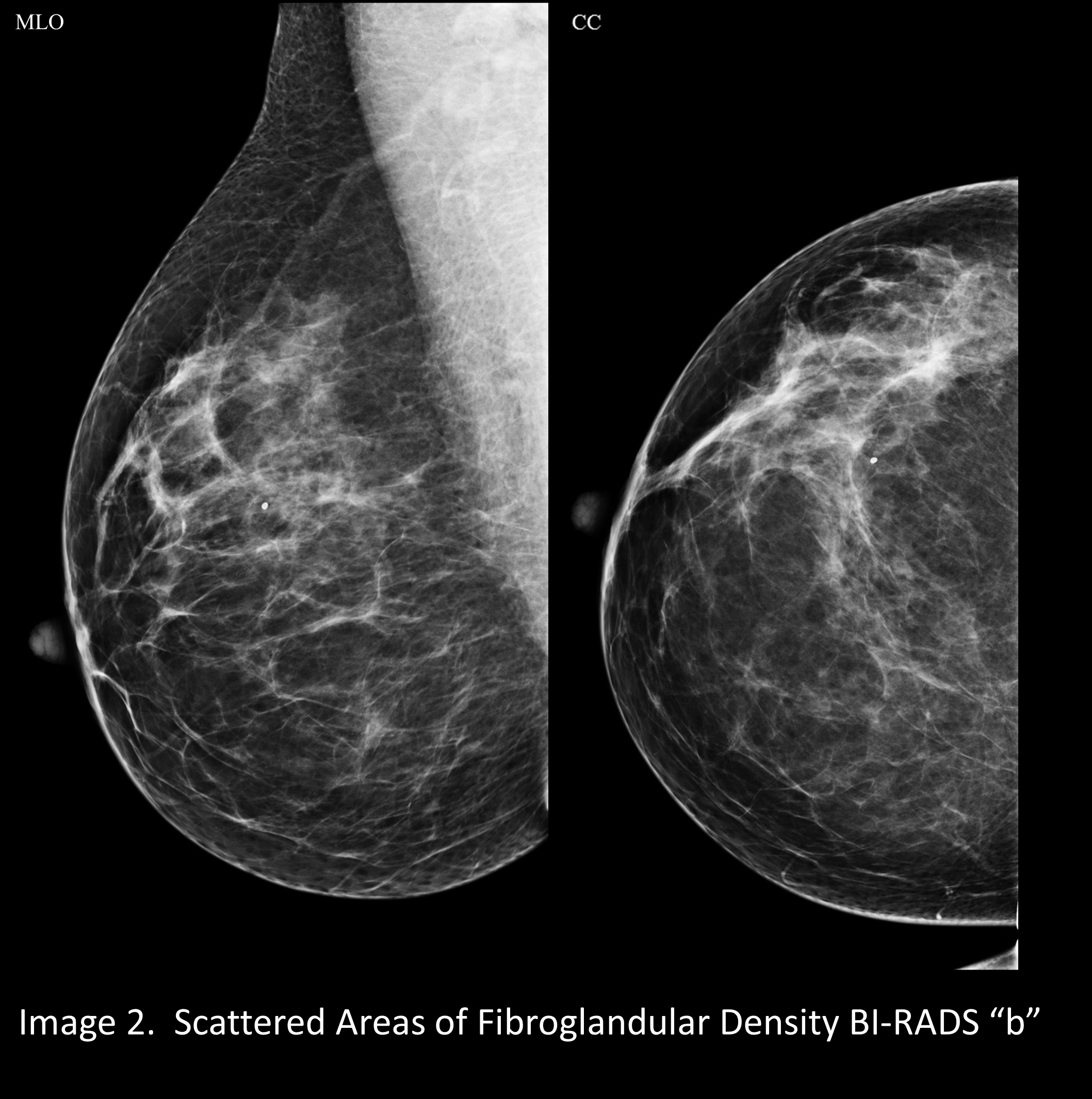
Understanding Scattered Fibroglandular Breast Tissue




Breast Density Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org



Fibroglandular Densities Mammographic Breast Density Itn
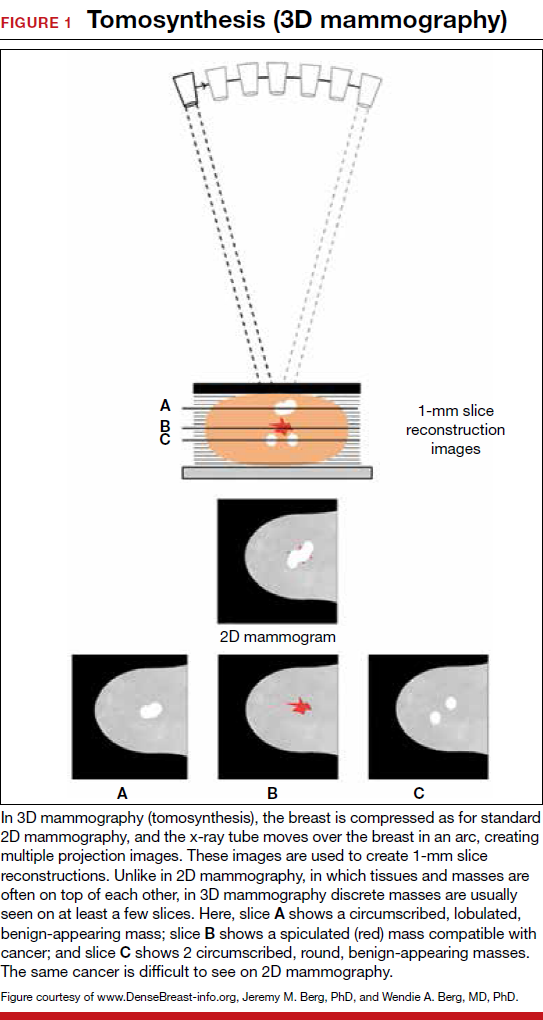



Breast Density And Optimal Screening For Breast Cancer Mdedge Obgyn




A 65 Year Old Woman Undergoes Average Risk Screening For Breast Cancer Download Scientific Diagram



Multimodality Imaging Of Breast Parenchymal Density And Correlation With Risk Assessment Springerlink




Ultimate Guide To Dense Breasts Mammoguide Learn Breast Imaging




Breast Density What Is It And What Does It Mean For Me Breast360 Org The American Society Of Breast Surgeons Foundation



Breast Density Explained Imaging Technology News




Many Women With Dense Breasts May Not Need Additional Screening National Cancer Institute



Common Mammogram Findings Moose And Doc




Patient Questions And Answers Densebreast Info Inc



How To Decrease Breast Density To Reduce Breast Cancer Risk Mammalive Foundation



Fibroglandular Densities Mammographic Breast Density Itn




Mammogram Images Understanding Your Results



Izotropic Corporation Izotropic Receives Notice Of Allowance For Measuring Breast Density From Us Patent Office



Cureus Hematoma Mimicking Breast Cancer On Ct Scan And Breast Ultrasound




Breast Density



3




Breast Density Testing In Rochester Ny Elizabeth Wende Breast Care




Dense Breasts Are You Educated Link




Digital Mammography And Computeraided Diagnosis 1 Breast Cancer



What Breast Density Means To You Stacey Vitiello M D




Breast Density Clinical Implications And Assessment Methods Radiographics




Dense Breast Tissue And Breast Cancer Risk



Fibroglandular Density What Every Woman Should Know
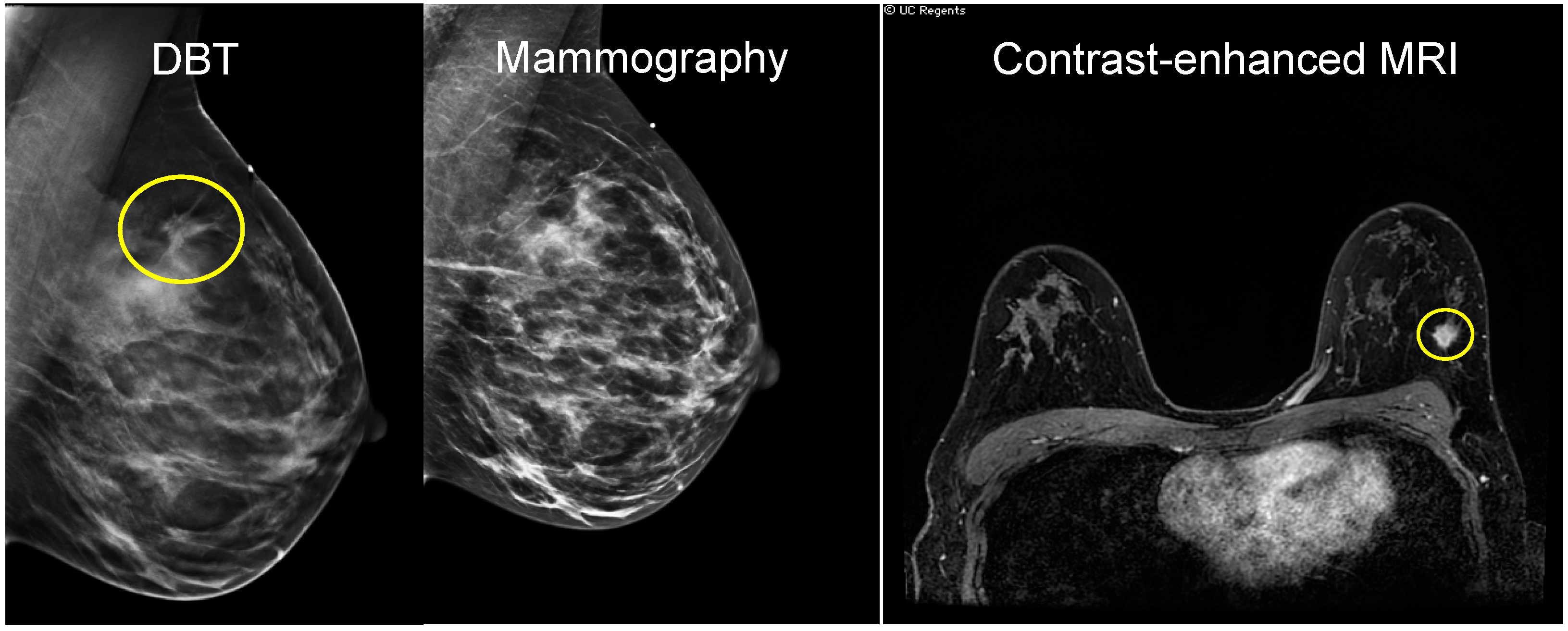



Cancers Free Full Text Current Landscape Of Breast Cancer Imaging And Potential Quantitative Imaging Markers Of Response In Er Positive Breast Cancers Treated With Neoadjuvant Therapy Html




Subject Mammography Standard Of Care




Should You Worry About Dense Breasts Everyday Health
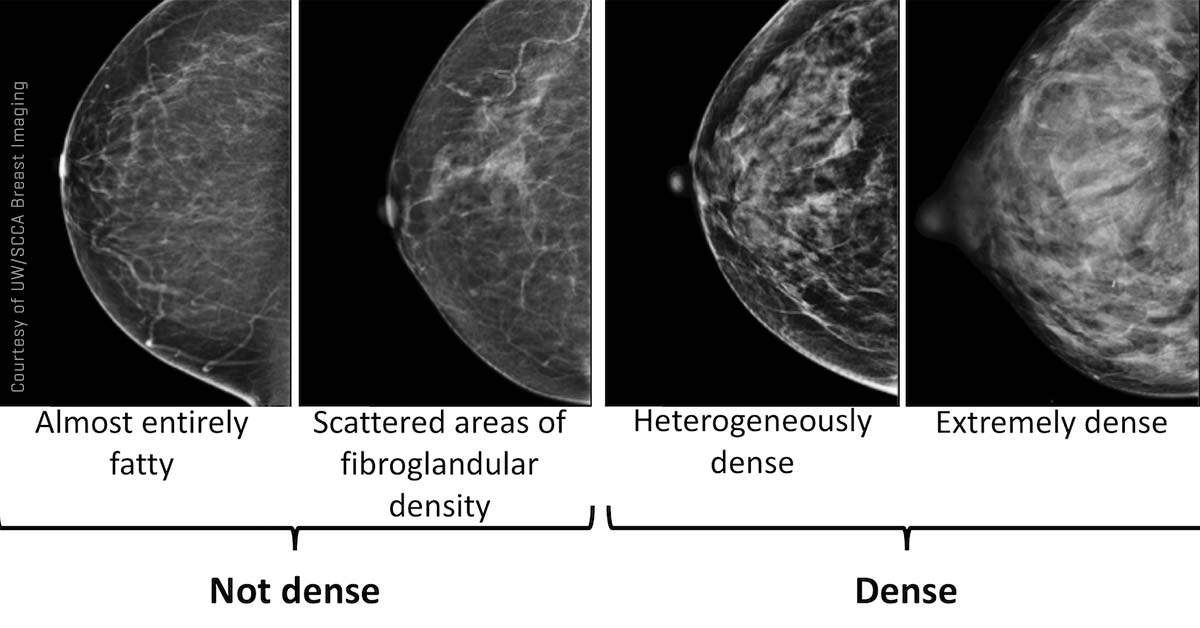



What S The Best Way To Screen Dense Breasts
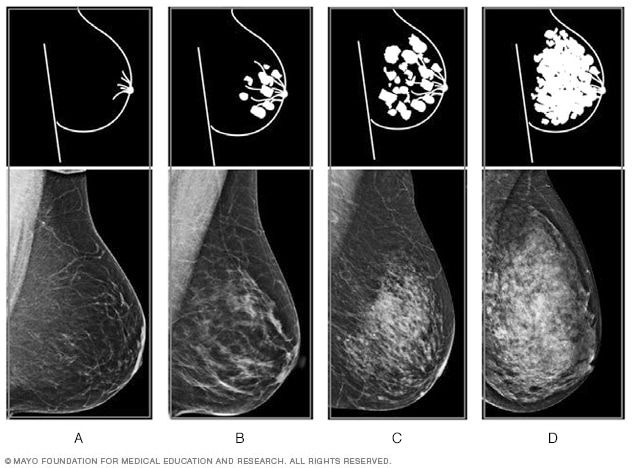



Dense Breast Tissue What It Means To Have Dense Breasts Mayo Clinic




My Doctor Says I Have Dense Breasts What Are Dense Breasts Johns Hopkins Medicine




Breast Density Canadian Cancer Survivor Network




Screening Ultrasound As An Adjunct To Mammography In Women With Mammographically Dense Breasts American Journal Of Obstetrics Gynecology
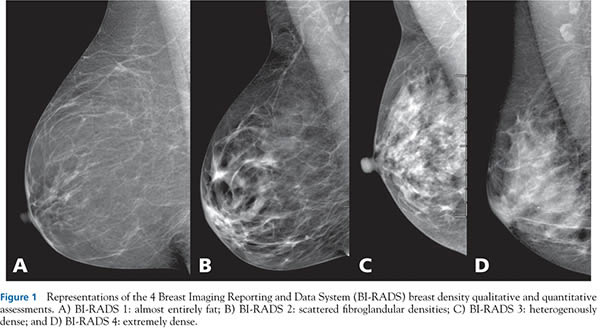



The Problem With Mandatory Breast Density Reporting Laws Scienceblogs




Patient Questions And Answers Densebreast Info Inc
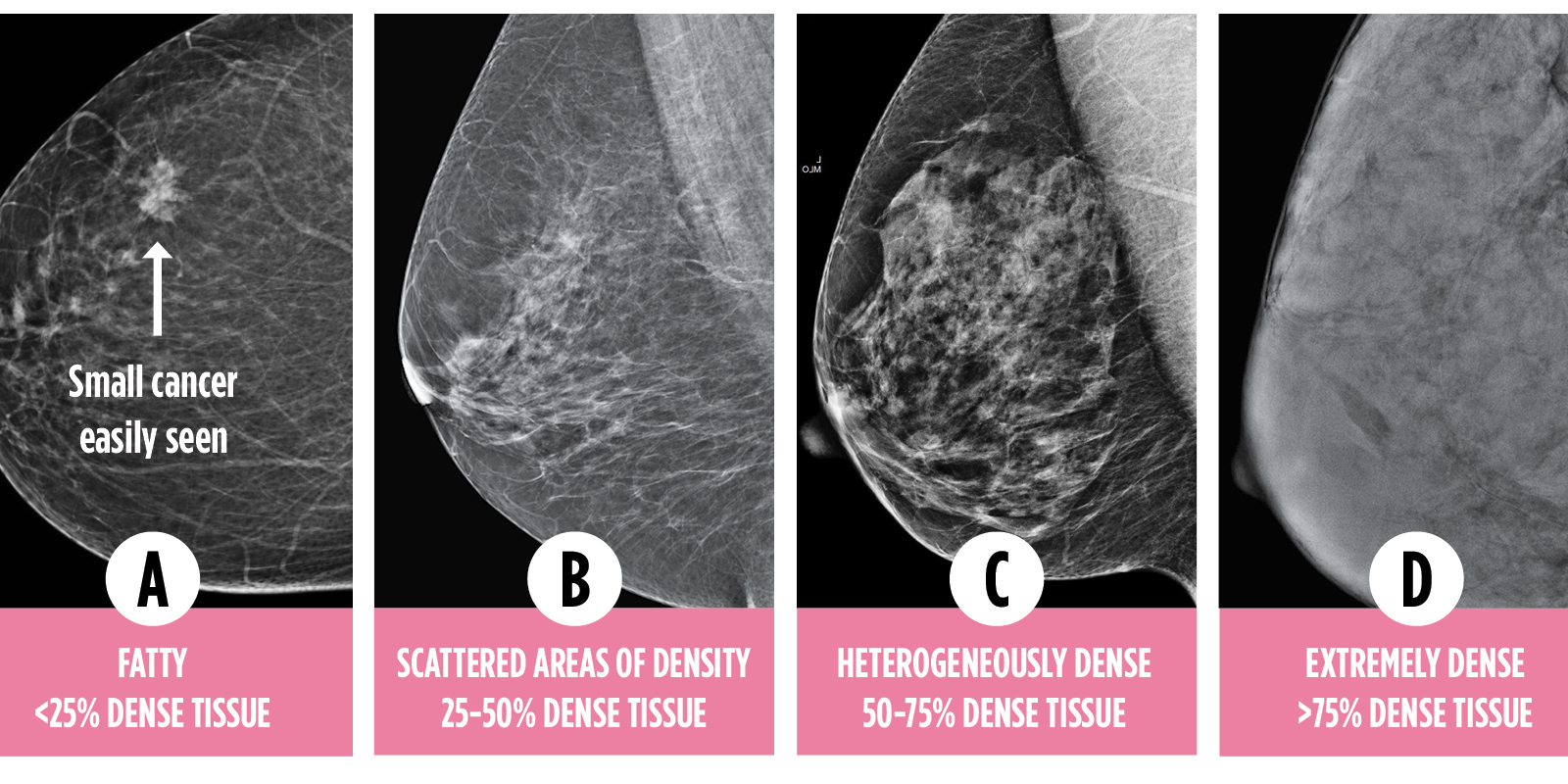



Get Informed Dense Breasts Canada Find Out Your Breast Density




The Relationship Of Breast Density In Mammography And Magnetic Resonance Imaging In High Risk Women And Women With Breast Cancer Clinical Imaging




Rad Tech Ce Asrt Arrt Ce Category A Credits Radiology Continuing Education



1
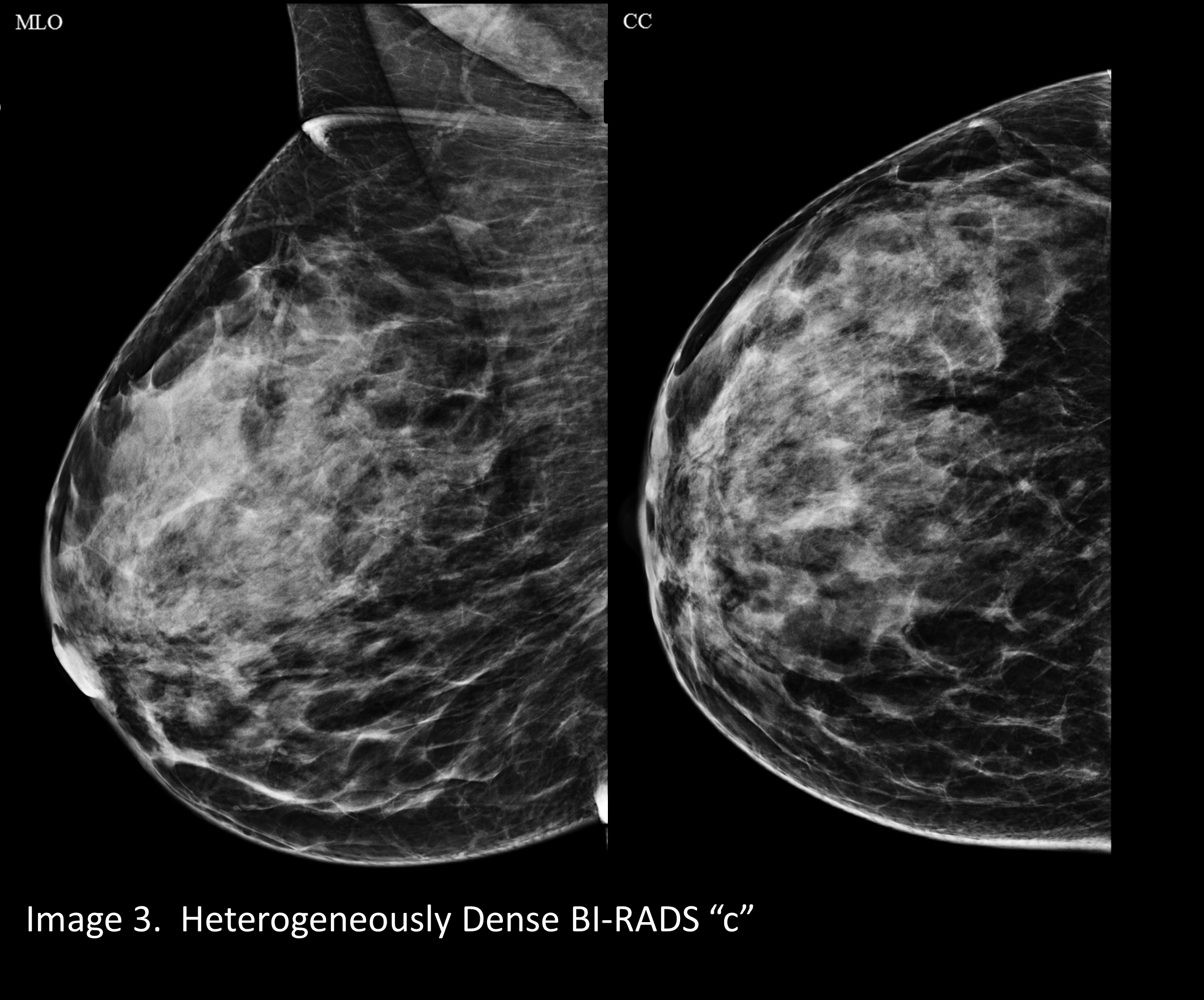



Your Patient Got A Dense Breast Notification With Her Mammogram Report What Are You Supposed To Do Christianacare News



What Breast Density Means To You Stacey Vitiello M D




The Evolution Of Breast Density Scales And Algorithms Densitas
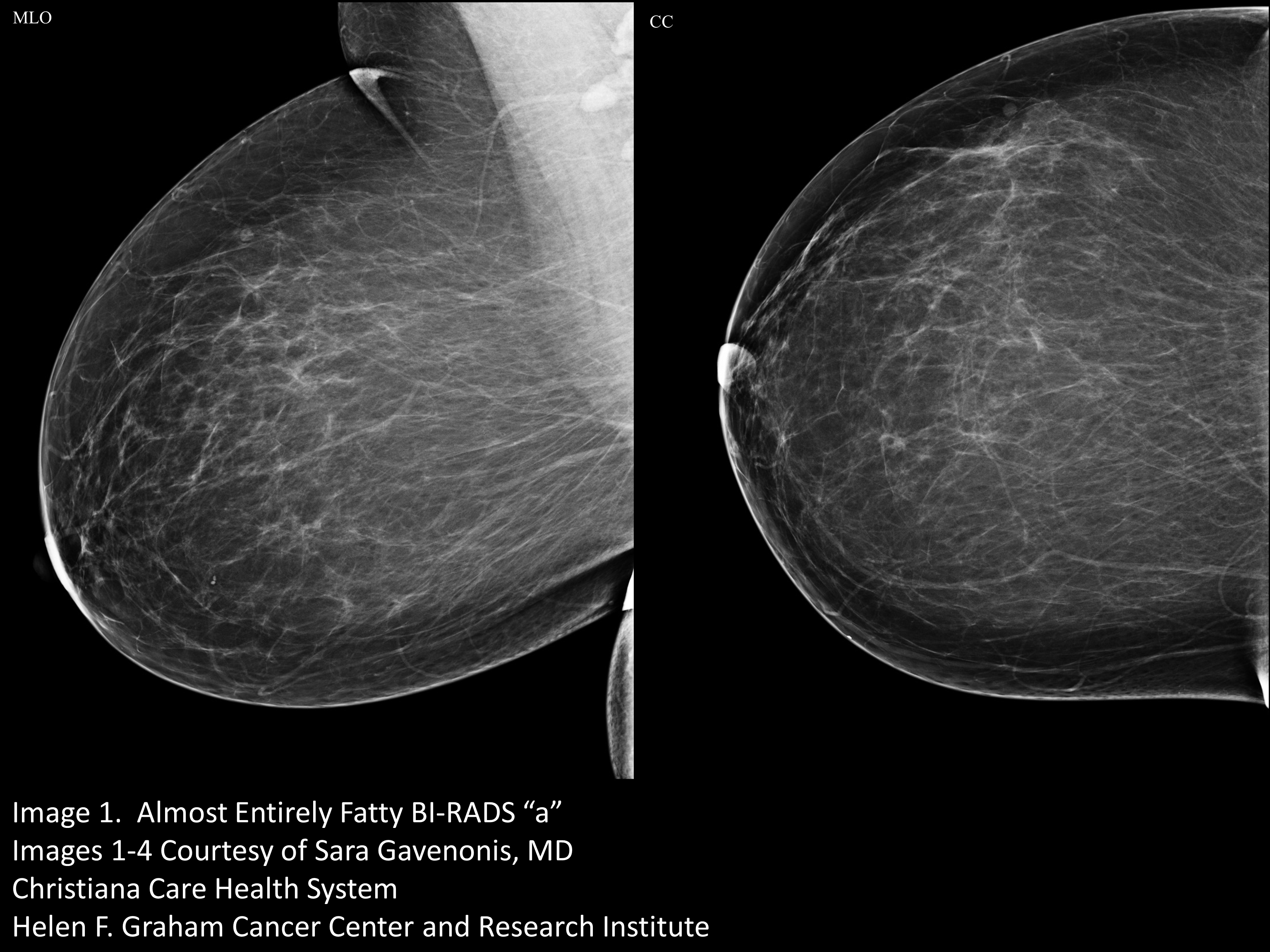



Your Patient Got A Dense Breast Notification With Her Mammogram Report What Are You Supposed To Do Christianacare News



What Breast Density Means To You Stacey Vitiello M D




Breast Density What Is It And What Does It Mean For Me Breast360 Org The American Society Of Breast Surgeons Foundation



Med Uvm Edu Docs Cms Breastdensitypresentation Medical Communications Documents Cms Breastdensitypresentation Pdf Sfvrsn 246c53 2




Fibroglandular Density Breast Density Fibrous Tissue Detection At Uh Breast Health Centers University Hospitals




Both Doctors And Patients Confused By Dense Breasts American Council On Science And Health
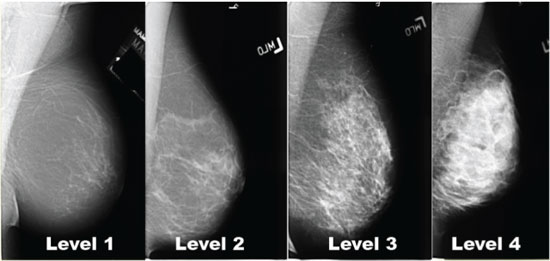



How Dense Are You Dennis R Holmes M D F A C S Breast Cancer Surgeon




Assessment Of Extent Of Breast Cancer Comparison Between Digital Breast Tomosynthesis And Full Field Digital Mammography Clinical Radiology
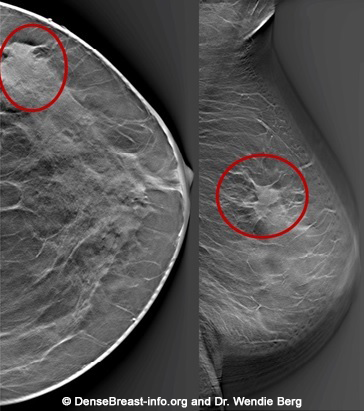



Mammography 3d Mammography Tomosynthesis Densebreast Info Inc




Breast Density The Breast Cancer School For Patients
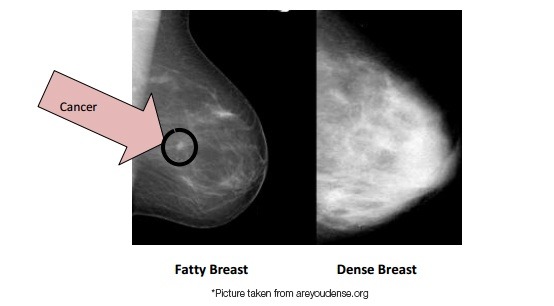



Are You Missing The Added Revenue Of Dense Breast Imaging Radiology Oncology Systems



3



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿